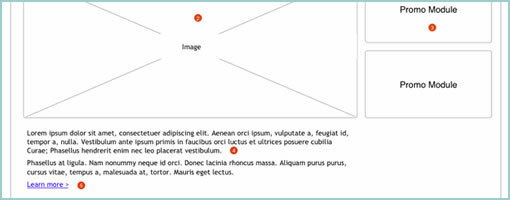
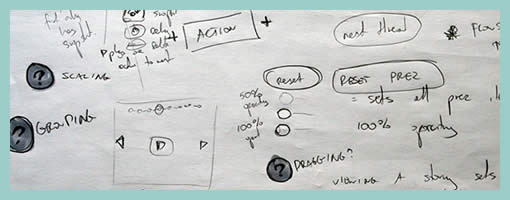
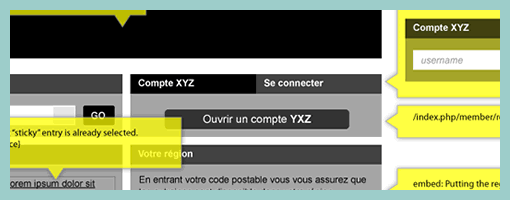
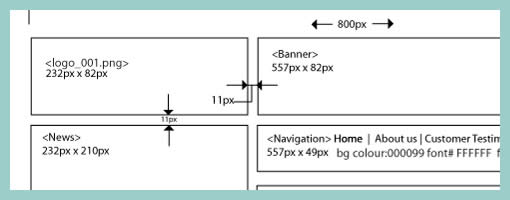
Traditional animators have been relying on sketching techniques of their own which I thought might be inspirational. Animators represent time with exposure sheets (aka. dope sheets) through which a large number of information can be conveyed to others. An x-sheet is pretty much a frame by frame representation of time to which notes can be layered on top. Some of these notes typically include information about: dialogue, camera angles, lighting, background and audio. Since timings of around 30 frames per second are standard, each xsheet is just a snapshot of a few seconds. Nevertheless, animators still find them useful as a communication artifact.
Here is what the people at Michael Sporn Animation studios have to say about these deliverables:
You see, when you get used to reading X-sheets, you see them as time. You don’t see the lines, you see seconds and footage, instantaneously. As an animator, you get an overview immediately of the scene; as a director you read the track, how the animator has constructed the scene, and what camera moves are indicated and why.
Here are a couple extra x-sheet samples.
Of course x-sheets work for a passive medium such as film and it’s questionable of how useful they might be for interactive web applications. Nevertheless, I still wonder if some of these ideas can be useful to our field. What other information can experience or interaction designers “layer” on top of the existing deliverables that we are typically accustomed to? Perhaps it would be interesting to combine a user flow representation with a learning curve or effort representation? What ever happened to representing sound in a UI sketch? What about a wireframe referencing an x-sheet sketch for the times when we do use animation? Hey, and what about a user flow with one axis dedicated to representing time consistently? Just thinking out loud.
Credits: Jun Falkenstein